金沢大学医薬保健研究域医学系の小野賢二郎教授らのグループは、金沢大学附属病院でレカネマブ(※1)治療を受けた100例の早期アルツハイマー病(※2)患者データを解析しました。タウ蓄積を反映するマーカーである脳脊髄液中リン酸化タウ181(Cerebrospinal fluid phosphorylated tau 181: CSF-ptau181)(※3)濃度とレカネマブの副作用のアミロイド関連画像異常(Amyloid related imaging abnormalities: ARIA)(※4)発現および、治療開始後の認知機能推移との関連を検討したところ、治療前のCSF-ptau181濃度が低値の方に比べて、高値の方は有意にARIA発現が多く、治療6カ月後、12か月後の認知機能低下が強いことを示しました。
レカネマブは、アルツハイマー病による軽度認知障害および軽度認知症の方が対象となる治療薬です。CSF-ptau181はアルツハイマー病において脳内のタウ蓄積を反映して上昇することが知られているタウマーカーです。本研究結果より、レカネマブ治療は脳内のタウ蓄積が少ないアルツハイマー病のより早期の患者で安全性および有効性が高い可能性が示唆されました。
これらの知見より、今後、CSF-ptau181測定が抗アミロイド抗体薬の治療効果予測および副作用リスクの層別化の促進に活用されることが期待できます。
本研究は 2025 年 11 月 24 日に国際学術誌『Alzheimer’s Research & Therapy』のオンライン版に掲載されました。
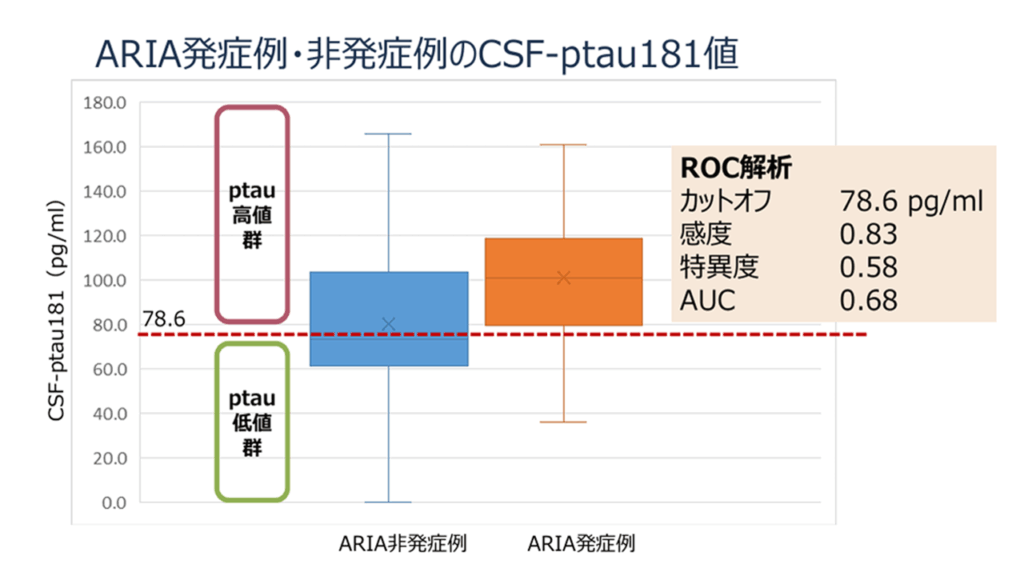
図:ARIA 非発現群、ARIA 発現群におけるレカネマブ治療前の CSF-ptau181 濃度
ARIA 発現群では非発現群に比べて有意に CSF-ptau181 濃度が高値でした。ROC 解析では、カットオフを 78.6 pg/ml としたとき感度 83%、特異度 58%、AUC 0.68 でした。
各群の略語:ARIA (amyloid related imaging abnormalities:アミロイド関連画像異常)、AUC (area under the curve: 曲線下面積)、CSF (cerebrospinal fluid:脳脊髄液)、p-tau 181 (phosphorylated tau protein 181:リン酸化タウ181)、ROC (receiver operating characteristic:受信者動作特性)
【用語解説】
※1 レカネマブ
レカネマブはアルツハイマー病の治療薬で、アミロイド β 凝集体の中でも、神経毒性が特に高いとされるアミロイド β プロトフィブリルに選択的に結合する抗体です。
※2 アルツハイマー病
アルツハイマー病は徐々に進行する脳の疾患で、記憶や思考する能力が徐々に障害され、やがて日常生活に支障をきたす認知症と呼ばれる状態に陥る病気です。アルツハイマー病の患者の脳内には、アミロイド β という物質が溜まってできる老人斑といわれる構造物や、異常な神経線維のもつれ(タウタンパクが異常リン酸化して生じる神経原線維変化)、神経細胞の消失といった変化が見られ、これらの変化が長い時間をかけて進行します。
※3 CSF-ptau181
脳脊髄液中リン酸化タウ 181(Cerebrospinal fluid phosphorylated tau 181: CSF-ptau181)の略語です。アルツハイマー病の病理所見である神経原線維変化は、過剰にリン酸化されたタウタンパク凝集体の蓄積が原因と考えられています。タウタンパクには、多くのリン酸化部位が知られています。特に、181 番目のスレオニン残基がリン酸化されたタウタンパク(ptau 181)は、アルツハイマー病でよく見られます。そのため、CSF-ptau 181がアルツハイマー病バイオマーカーとして使用されています。
※4 ARIA
アミロイド関連画像異常(amyloid related imaging abnormalities:ARIA)の略語です。アルツハイマー病治療薬であるレカネマブなどのアミロイド β 抗体療法に関連して生じるMRI 所見の異常で、ほとんどの場合は症状を伴いませんが一部で頭痛や錯乱などの症状が起こります。
ジャーナル名:Alzheimer’s Research & Therapy
関連情報
金沢大学大学院医薬保健学総合研究科・医薬保健学域医学類:https://www.med.kanazawa-u.ac.jp/index.html






 PAGE TOP
PAGE TOP